What Is Retinoblastoma?
Retinoblastoma is a type of paediatric cancer that affects the retina of the eye. Your retina collaborates with your brain to assist you in seeing. The retina is located behind the pupil of the eye. It is made up of layers of cells that detect light and transmit information to your brain.
Retinoblastoma almost always occurs in children under the age of five.Retinoblastoma (RB) is the most common intraocular malignancy in children Cryotherapy, chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery are all treatments for retinoblastoma. The prognosis is determined by several factors, including the size and location of the tumour, as well as whether the cancer has spread. Most children with retinoblastoma live cancer-free after treatment if the tumour has not spread beyond the eye.
What is the prevalence of retinoblastoma?
Worldwide, about 8000 children are newly diagnosed with retinoblastoma every year (1in16,000 -18,000 live births). As per the Population Based Cancer Registries of India, the incidence rate in 0-4years age group is higher, ranging from 5.1 to 21.7 per million among males, and 3.4 to 18.9 per million among females. (2)
The condition usually affects only one eye. About a quarter of the time, both eyes are affected.
What causes retinoblastoma?
Retinoblastoma is caused by both germline and somatic mutation in RB1 gene, a tumor suppressor gene located in the long arm of chromosome 13. The mutation causes uncontrollable growth of cells in the eye, eventually forming a tumour. A child inherits the RB1 mutation from a parent roughly 40% of the time (heritable retinoblastoma).. In those cases, healthcare providers are unsure what caused the genetic mutation (nonheritable retinoblastoma).
Almost80% of children with heritable retinoblastoma will develop tumours in both eyes (bilateral), while 15% will develop a tumour in only one eye and 5% will develop trilateral retinoblastoma (bilateral retinoblastoma and a brain tumour).Nonheritable retinoblastoma causes tumours in only one eye in children (unilateral).
What signs and symptoms indicate retinoblastoma?
The first sign of retinoblastoma is usually a change in the appearance of the eye. The symptoms can affect either one or both eyes. Symptoms of retinoblastoma include:
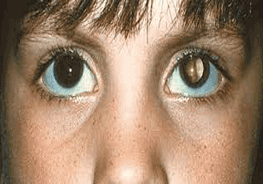
- Leukocoria (white pupil): Leukocoria is usually the first sign of retinoblastoma. The pupil appears white or cloudy (the round, black centre of the coloured part of the eye).
- Strabismus (crossed eyes): The eyes may appear misaligned, or one eye may turn in a different direction than the other. Strabismus can be mild to severe.
- Proptosis( eye bulging out) and loss of vision in advanced cases.
How is retinoblastoma identified?
- MRI scans and ultrasounds both produce detailed images of your child's eyes
- Cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF) analysisand bone marrow biopsy may be advised in advanced cases to determine whether the cancer has spread to the brain and bone marrow.
A specialized eye examination is usually used to diagnose retinoblastoma. Your child will be sedated during the examination. Your child is given medicine through a vein and falls asleep during the exam. The retina is examined by the eye doctor using instruments and lights.
Your child's doctor may also conduct imaging studies or other tests to determine whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Among these tests are:
What are the different stages of retinoblastoma?
Staging is a method used by Doctor to find out the extent of the disease and to classify retinoblastoma. They look at where the tumour is and whether it has spread to other parts of the body, such as the brain, bones, or organs. The majority of retinoblastoma tumours are detected before they spread throughout the body.
The team of providers who care for your child uses staging information to determine the best treatment plan for them. There are different staging systems. Commonly used system for intra ocular staging is Intraocular Classification of Retinoblastoma Grouping (ICRB). This staging system has divided the RB into 5 groups (A to E) depending on the extent of tumor inside the eye.
What is the treatment for retinoblastoma?
Treatments vary according to the stage of the disease.
Your child's medical team will consider whether cancer is limited to the eye (intraocular retinoblastoma). If it has spread to other parts of the body, treatments may differ (extraocular retinoblastoma). Treatments for retinoblastoma include:
- Chemotherapy involves the administration of chemotherapy drugs through an artery directly into the tumoror systemic chemotherapy through vein. Cancer cells are prevented from multiplying by the drugs. Chemotherapy may be administered to your child over the course of several weeks or months.
- Cryotherapy (cryoablation): Cryotherapy is a treatment that uses extreme cold (typically liquid nitrogen) to kill cancer cells.
- Photocoagulation and thermotherapy are examples of laser procedures. Heat is used by providers to destroy tumours with lasers.
- Plaque brachytherapy (a type of radiation therapy) may be recommended by your child's provider to treat retinoblastoma. Providers place a plaque (a tiny device) over the tumour on the eyeball. The plaque delivers radiation directly to the tumour over a period of several days. After treatment, the plaque is removed, and the tumour shrinks over time.
- Large tumours may necessitate the removal of the entire eyeball as well as a portion of the optic nerve behind the eyeball. This procedure is known as enucleation. The provider can insert an artificial eyeball and lens (similar to a contact lens) into your child's eye socket.
Is it possible to prevent retinoblastoma?
Nonheritable retinoblastoma cannot be prevented.
If you or your partner had retinoblastoma as a child, your children have a 50% chance of inheriting the disease. If you have a family history of retinoblastoma or the RB1 gene mutation, you should think about genetic testing before having children. Children with a retinoblastoma family history should have regular eye exams beginning at birth. It is critical to detect and diagnose retinoblastoma as soon as possible. An early diagnosis can improve the prognosis significantly. Early detection of cancer may prevent vision loss.
For enquiries, bookings or support, call us at +91-96508 06846
Need help? Get a call back from our support team
Contact Us

